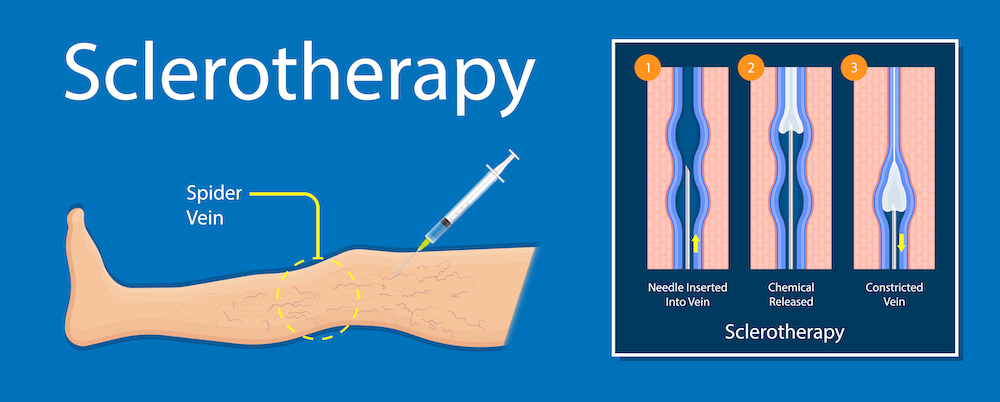
Sclerotherapy is a widely-used medical procedure designed to eliminate varicose veins and spider veins, providing both cosmetic and therapeutic benefits. Here’s an in-depth look at what sclerotherapy entails, its benefits, the procedure, and what you can expect during recovery.
What is Sclerotherapy?
Sclerotherapy involves the injection of a sclerosing solution directly into the affected veins. This solution causes the vein walls to stick together, which eventually leads to the vein collapsing and being reabsorbed by the body. The blood flow is naturally rerouted through healthier veins, resulting in improved circulation and the disappearance of the unsightly veins.
Benefits of Sclerotherapy
-
Cosmetic Improvement: Sclerotherapy is highly effective in reducing the appearance of varicose and spider veins, leading to smoother, clearer skin.
-
Symptom Relief: Many patients experience relief from symptoms associated with varicose veins, such as aching, swelling, and cramping.
-
Minimally Invasive: The procedure is relatively simple and minimally invasive, usually performed in an outpatient setting with minimal downtime.
-
Long-Lasting Results: With proper post-treatment care, the results of sclerotherapy can be long-lasting, although new veins may develop over time.
The Sclerotherapy Procedure
-
Initial Consultation: During your initial consultation, a healthcare provider will assess your veins and overall health to determine if you are a suitable candidate for sclerotherapy. This may include a physical examination and possibly an ultrasound.
-
Preparation: On the day of the procedure, you may be advised to avoid certain medications or activities. It’s important to wear loose, comfortable clothing.
-
Injection Process: The procedure itself involves injecting the sclerosing solution into the affected veins using a fine needle. The number of injections depends on the size and number of veins being treated. The process usually takes 30 to 45 minutes.
-
Post-Procedure Care: After the injections, you may be instructed to wear compression stockings to aid in the healing process and improve blood flow. Walking and light activity are generally encouraged, but strenuous activities should be avoided for a few days.
Recovery and Results
-
Immediate Effects: You may experience some mild discomfort, bruising, or swelling at the injection sites. These side effects are typically short-lived.
-
Gradual Improvement: The treated veins will gradually fade over several weeks or months. Multiple treatments may be necessary for optimal results, depending on the severity of the vein issues.
-
Follow-Up: Follow-up appointments are essential to monitor the progress and determine if additional treatments are needed.
Potential Risks and Side Effects
While sclerotherapy is generally safe, there are some potential risks and side effects to be aware of:
-
Allergic Reactions: Though rare, some patients may have an allergic reaction to the sclerosing solution.
-
Skin Changes: Temporary skin discoloration or the development of small blood vessels (matting) near the treated area can occur.
-
Blood Clots: In rare cases, blood clots can form in the treated veins or in deeper veins.
-
Ulcers: Ulcers at the injection site can develop, though this is uncommon.
Who is a Good Candidate for Sclerotherapy?
Sclerotherapy is suitable for most people with varicose or spider veins, but certain conditions may make the procedure inappropriate, such as:
- Pregnancy or breastfeeding
- A history of blood clots or deep vein thrombosis
- Allergies to the sclerosing solution
- Certain chronic health conditions