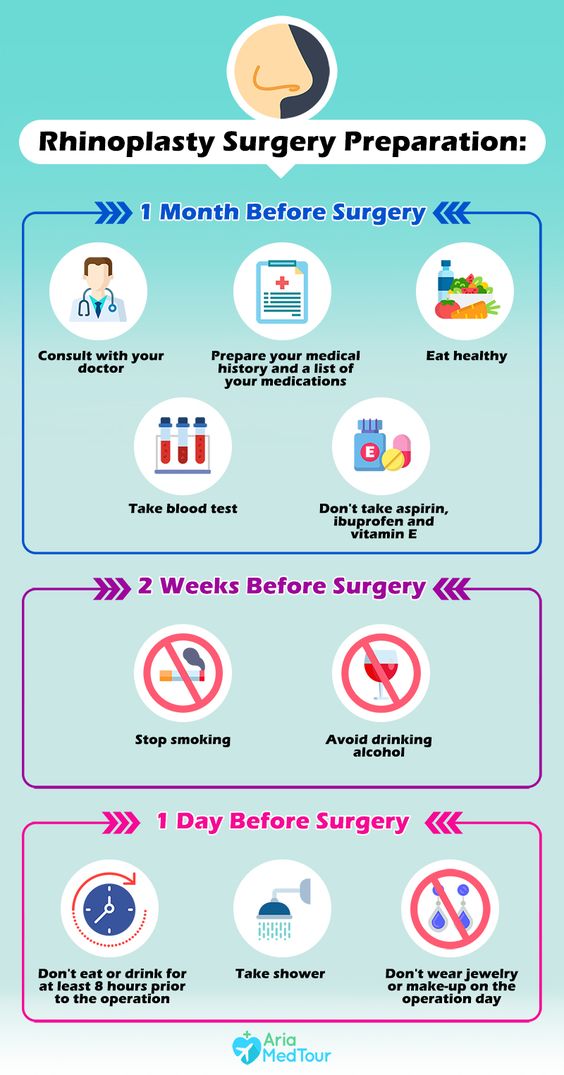
Rhinoplasty, commonly known as a nose job, is one of the most sought-after cosmetic procedures worldwide. It offers both aesthetic and functional benefits, making it a versatile treatment for those looking to enhance their appearance or improve nasal function. This article delves into what rhinoplasty entails, the reasons people opt for it, the procedure itself, and the recovery process.
What is Rhinoplasty?
Rhinoplasty is a surgical procedure that alters the shape of the nose. It can be performed for cosmetic reasons, such as changing the nose's size, shape, or proportions, or for medical reasons, like correcting breathing issues related to structural defects.
Reasons for Rhinoplasty
People seek rhinoplasty for various reasons, including:
- Cosmetic Enhancements: To change the size, shape, or angle of the nose, improve facial symmetry, or address imperfections such as a hump or drooping tip.
- Functional Improvements: To correct nasal obstructions, such as a deviated septum, that cause breathing difficulties.
- Reconstructive Purposes: After trauma or injury, to restore the nose's original appearance and function.
The Rhinoplasty Procedure
Rhinoplasty is typically performed under general anesthesia and can take anywhere from one to three hours. The surgery involves either an open or closed approach:
- Open Rhinoplasty: An incision is made across the columella (the tissue between the nostrils), allowing for better access and visibility of the nasal structure.
- Closed Rhinoplasty: Incisions are made inside the nostrils, resulting in no visible scars. This method is less invasive but may be limited in the extent of changes it can achieve.
Recovery and Results
Post-surgery, patients can expect some swelling and bruising around the nose and eyes, which usually subsides within a few weeks. Most people can return to normal activities within two weeks, but it may take up to a year for the nose to fully heal and for the final results to become apparent.
Risks and Considerations
As with any surgical procedure, rhinoplasty carries risks, including infection, bleeding, and anesthesia complications. It’s essential to consult with a qualified surgeon who can provide a thorough assessment and realistic expectations.