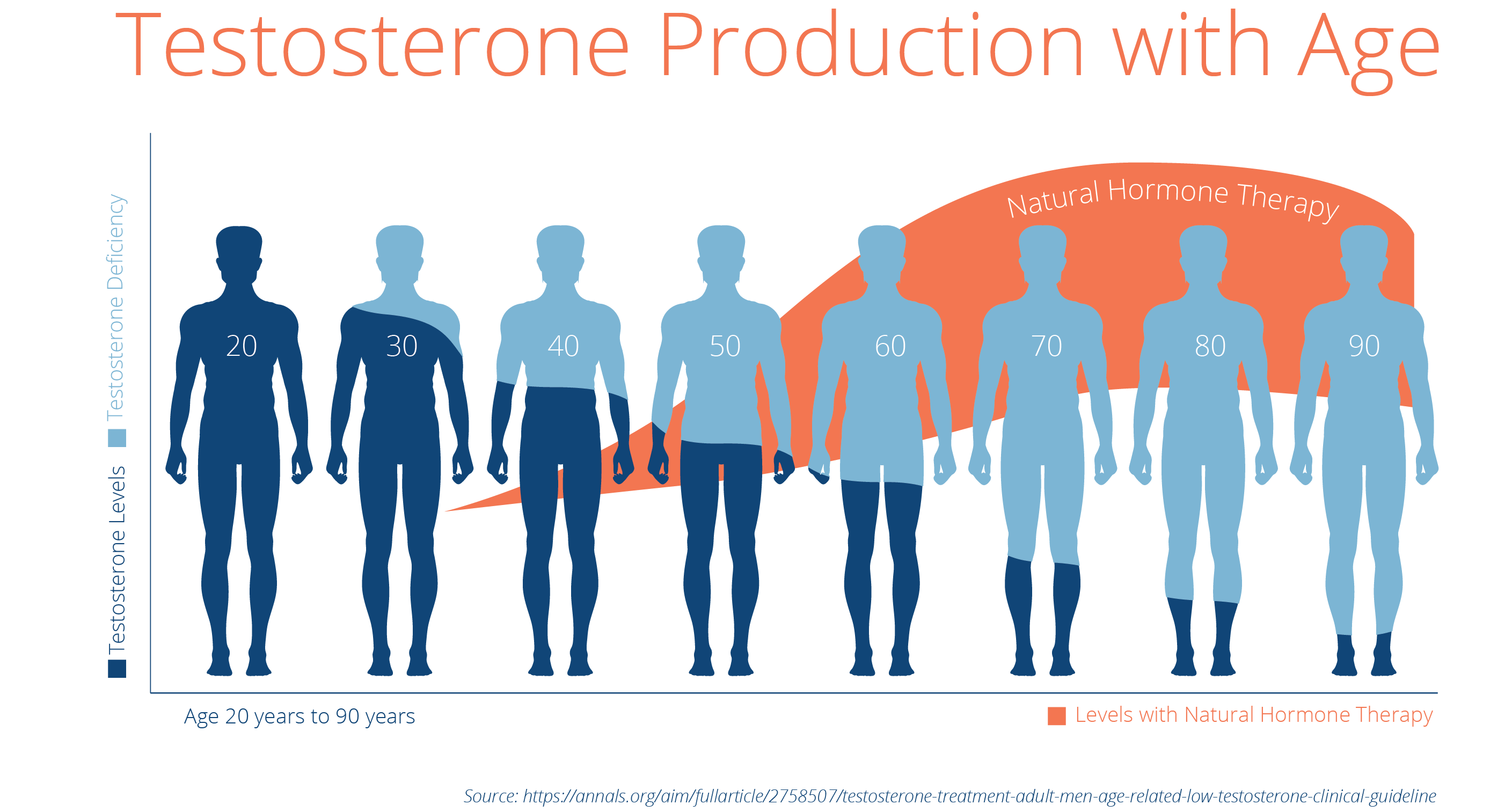
Testosterone is often referred to as the "male hormone," but its influence extends far beyond gender. This powerful hormone plays a crucial role in various bodily functions, affecting both men and women. Understanding testosterone's impact on health, from physical strength to mood regulation, is essential for maintaining overall well-being.
The Role of Testosterone:
Testosterone is primarily produced in the testes in men and the ovaries in women, with small amounts also produced by the adrenal glands. It is responsible for the development of male characteristics such as muscle mass, facial hair, and a deeper voice. In women, testosterone helps regulate libido, bone density, and muscle strength.
Health Impacts of Testosterone Levels:
Balanced testosterone levels are key to a healthy life. Low testosterone, or hypogonadism, can lead to a variety of health issues, including:
-
Reduced Muscle Mass and Strength: Testosterone is vital for muscle growth and maintenance. Low levels can result in decreased muscle mass, leading to weakness and fatigue.
-
Bone Density: Testosterone plays a crucial role in bone health. Insufficient levels can increase the risk of osteoporosis and fractures.
-
Mood and Mental Health: Testosterone influences mood and cognitive function. Low levels have been associated with depression, irritability, and cognitive decline.
-
Sexual Health: Testosterone is essential for sexual function. Low levels can lead to reduced libido, erectile dysfunction in men, and diminished sexual satisfaction in women.
Managing Testosterone Levels:
Maintaining optimal testosterone levels is crucial for overall health. This can be achieved through a combination of lifestyle changes, such as:
-
Regular Exercise: Resistance training and high-intensity interval training (HIIT) are particularly effective in boosting testosterone levels.
-
Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in proteins, healthy fats, and micronutrients like zinc and vitamin D supports testosterone production.
-
Adequate Sleep: Quality sleep is essential for hormone production, including testosterone.
-
Stress Management: Chronic stress can lead to elevated cortisol levels, which can suppress testosterone production.