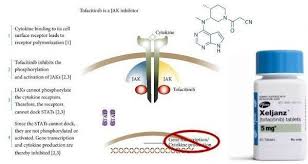
Xeljanz, known generically as tofacitinib, is a medication that has gained significant attention in the medical community for its role in treating various autoimmune conditions. Developed by Pfizer, Xeljanz belongs to a class of drugs called Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors. This article explores the uses, benefits, and potential risks associated with Xeljanz, providing a comprehensive overview for both patients and healthcare professionals.
What is Xeljanz?
Xeljanz is an oral medication primarily used to treat conditions like rheumatoid arthritis (RA), psoriatic arthritis (PsA), and ulcerative colitis (UC). It works by inhibiting the activity of certain enzymes (JAK1 and JAK3) involved in the inflammatory processes of the immune system. By doing so, Xeljanz helps reduce inflammation, pain, and damage caused by these chronic autoimmune diseases.
Approved Uses
-
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): Xeljanz is often prescribed for adults with moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis who have not responded well to methotrexate. It helps in reducing joint pain, swelling, and improving physical function.
-
Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA): For patients with PsA, Xeljanz can reduce the number of tender and swollen joints, alleviate symptoms, and improve overall quality of life.
-
Ulcerative Colitis (UC): Xeljanz is also approved for adults with moderate to severe ulcerative colitis who have not had success with other medications. It helps to achieve and maintain remission, reducing the need for corticosteroids.
Benefits of Xeljanz
The primary benefit of Xeljanz lies in its ability to provide relief from the symptoms of autoimmune diseases. Many patients experience a significant reduction in pain and inflammation, leading to improved mobility and quality of life. For those with ulcerative colitis, Xeljanz offers the possibility of achieving remission, which can be life-changing.
Potential Risks and Side Effects
While Xeljanz can be highly effective, it is not without risks. Common side effects include headaches, upper respiratory tract infections, and diarrhea. However, more serious side effects have been reported, including an increased risk of blood clots, infections, and certain cancers. Due to these risks, the FDA has issued a boxed warning for Xeljanz, and it is typically prescribed when other treatments have failed or are not suitable.
Patient Considerations
Patients considering Xeljanz should have a detailed discussion with their healthcare provider about the potential benefits and risks. Regular monitoring through blood tests is often required to ensure the medication is working effectively and to catch any adverse effects early. It's also important for patients to inform their doctor of any other medications they are taking, as Xeljanz can interact with other drugs.